HEPATITIS - B
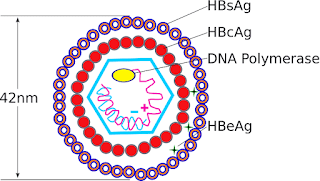
HEPATITIS - B It is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic disease On electron microscope view virus is either spherical or tubular in shape HBsAg - surface antigen HBcAg - core antigen → found in nucleus of hepatocytes but never found in blood however antibody to it is seen in blood HBV DNA HBeAg - marker for replication/infectivity of virus Pre - core mutant = HBeAg absent - More severe - Replication not detected routinely ROUTE OF TRANSMISSION: Most commonly - percutaneous route : sexual transmission Blood transfusion Vertical transmission - mother to baby Accidental needle stick injury SERUM MARKERS: HBsAg - - first to appear 1 - 12 weeks of infection - earliest serological evidence of hepatitis - B infection - precedes SGPT increases = 2 - 6 weeks - sequence of appearance HBsAg positive → SGPT increases → jaundice → disappear in reverse direct...