ACROMEGALY

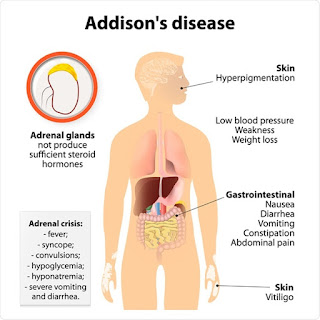
ACROMEGALY It is a disorder that results from excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed (excess GH after puberty) It is a diseases of anterior pituitary Somatotrophs are abundant cells in pituitary somatotroph adenoma is most common cause of developing Acromegaly Mammosomatotroph adenoma growth hormone and prolactin increases clinical features : Galactorrhea Leading cause of extra pituitary source of excess growth hormone → pancreatic adenoma (islet cells tumor) Leading cause of excessive GHRH production → CARCINOID TUMOR CLINICAL FEATURES : ACRAL ENLARGEMENT : Increase in size of hand/feet Increase in finger thickness leading to spade like hands Lower Jaw prominence called as Prognathism Frontal Bossing Heel pad thickness >21 mm → used for monitoring growth in these patients Coarse facies / deep hollow voice ,Hyperhidrosis(excessive sweating) , sebum increase (increase incidence of acne) , ac...