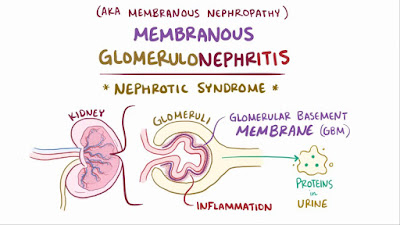
LIDDLE SYNDROME
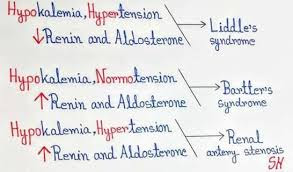
LIDDLE SYNDROME It is a AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT disorder It involving increased activity of the epithelial sodium channel(ENaC) Causes hypertension → negative inhibition of RAAS( renin angiotensin aldosterone system) system → renin decreased → aldosterone decreased By this feedback mechanism aldosterone levels are decreased but hypertension occur due to excess salt and water in the body secondary to excessive activity of epithelial sodium channel Imaging : shows normal adrenal gland DOC : AMILORIDE (inhibit function of epithelial sodium channel