BRONCHIECTASIS

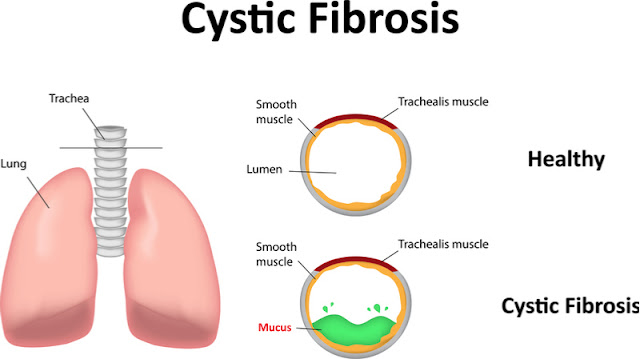
Bronchiectasis : Destruction / Dilatation of large airways - airways are filled with pus results in the features of bronchorrhea HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EXAMINATION: CYLINDRICAL / TUBULAR - MOST COMMON subtype - Represents airways are dilated and thick walled which filled with pus by the dangerous organisms like pseudomonas. this organism later will form the biofilm in the lungs which results in antibiotic resistant. expansion of pus filled cavity will erode the blood vessels of lungs which results is massive hemoptysis and death of the patient. Cause of death - Massive hemoptysis Causes : A) FOCAL - Obstruction which subsequently cause infection in the airway and results in pus. following condition can cause focal bronchiectasis - Foreign body aspiration (children) - Pulmonary hamartoma (adults) - Bronchial carcinoid (adults) note: Benign tumor in adults like pulmonary hamartoma and carcinoid tumors which encroached the bronchus and result in obstruction of airways and causes ate...