Hyperthyroidism is the condition that occur due to excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland.
CAUSES :
A) PRIMARY HYPERTHYROIDISM
Most common cause of PRIMARY HYPERTHYROIDISM is GRAVE'S DISEASE
GRAVE'S DISEASE
↓
Have L.A.T.S - Ab (Long acting thyroid stimulating antibody)
identical to TSH
↓
Resulting in INCREASE T4 , INCREASE T3 , DECREASE TSH
B) SECONDARY HYPERTHYROIDISM
Due to Pituitary adenoma ⇢ INCREASED TSH , INCREASED T3 , INCREASED T4
C) TOXIC NODULAR GOITER
Frequent in areas of iodine deficiency
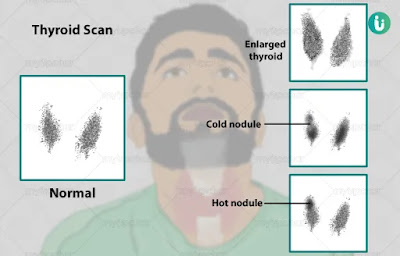
Diagnosed by Thyroid scan using I - 123/I - 132
Warm nodule ⇒ Normal uptake
Cold nodule ⇒ suggestive of malignancy
Hot nodule ⇒ over active tissue
D) JOD BASEDOW EFFECT :
Seen with intake of iodized salt for long duration in iodine replete population.
Has upgrade of [iodine trapping leading to increase production of T4/T3.
E) THYROTOXICOSIS FACTITIA :
It is Thyrotoxicosis occurring due to any other cause other than high salt intake.
example: seen in patient consuming poor quality beef containing thyroid gland of animals
F) STRUMA OVARI :
Ovarian tumor synthesizing hormones
G) GESTATIONAL TROPHOBLASTIC NEOPLASIA ;
HCG ∝ TSH
Thus, HCG can bind to TSH receptors and stimulate them
CLINICAL FEATURES :
1. Sympathomimetics (+) : Palpitations, fine tremors, sweaty palms/soles ,hypertension
2. BMR Increased resulting in weight loss
3. Calorigenesis Increased causes HEAT INTOLERANCE
4.Females⇾ oligomenorrhea /infertility
5. Proptosis ( due to retrobulbar fat deposition )⇢ blinking action inadequate ⇢ results in drying of cornea ⇢ EXPOSURE KERATITIS
ON EXAMINATION
1. Sleeping pulse rate increased (most reliable sign)
2. Resting Tachycardia
3. Fine tremors
4. Pretibial Myxedema
5. Pemberton sign : On rising arms, there will be facial congestion due to compression of SVC by retrosternal goiter
WORKUP:
= Thyroid function test - total T4 and T3 increased , free T4,T3 increased
= TSH
- If TSH LOW - Primary hyperthyroidism (most common GRAVE'S) - further investigations are
- LATS titer
- Thyroid scan
- USG abdomen (females pt to rule out ovarian or uterine tumor)
-If TSH HIGH - Secondary hyperthyroidism - pituitary adenoma - diagnosis MRI head
TREATMENT :
1. Anti Thyroid Drugs : PROPYLTHIOURACIL (PTU)
propranolol for symptomatic management
Total thyroidectomy in case of poor response to medical therapy
2. Ablation of thyroid gland using Radioiodine I - 131
Secondary Hyperthyroidism due to pituitary adenoma - Trans-sphenoidal surgery






Comments
Post a Comment